Are Lab Diamonds Real? A Comprehensive Guide
December 4th, 2023 / Alese Oldenburg
The advancement of technology has led to many powerful and significant advancements, one of which is with direct application to the diamond industry. Technological capabilities have granted us the opportunity to create man-made diamonds that are now wonderful alternatives to traditionally mined diamonds. This development has opened up a plethora of options for consumers looking for lab grown diamond wedding bands, engagement rings, or other jewelry in terms of quality, price, and environmental concerns.
However, unfortunately, misinformation swirls around the internet about lab grown diamonds and their true nature, which can make it hard to decipher fact from fiction. It’s important for consumers to understand the truth about different lab diamond options, so they can be fully informed when approaching a diamond purchase. Many are still lost in the question, are lab grown diamonds real? Are they the same as real diamonds? To answer this question, we must first understand what makes organic and manmade diamonds unique.
Are Lab Created Diamonds Real?

In short, yes, lab diamonds are both a real and beautiful alternative to natural diamonds. Many lab diamond options look very similar to natural diamonds to the eye of the everyday consumer. However, there are distinct characteristics between the lab created and natural variety that set them apart from each other.
Natural Diamonds
The most notable factor is, of course, their formation, creation and acquisition. The answer to the question, how are diamonds made, can best help shed light on the differing qualities. A natural diamond has developed over millions of years below the earth’s surface at depths up to 150 to 200 kilometers. Under intense pressure and extremely high temperatures, the carbon compounds beneath the earth harden together, producing the beautiful stone that is revered today. To obtain these diamonds, the stones are mined from the ground through labor-intensive methods that have a major impact on both the environment and human labor conditions.
Lab Diamonds
In contrast, lab diamonds have been created by a new and unique method. This technological process was created with the aim to make beautiful diamonds at a lower cost and help circumvent the impact that a natural diamond has on the earth. Made in a highly-controlled laboratory, lab diamonds are subject to conditions that seek to imitate the high pressure and temperature environment found in nature.However, not all lab diamonds are the same. This is the second unique differentiation between diamond simulants and mined diamonds. Organic diamonds are formed almost entirely of carbon, which give them the shining properties they exude. Depending on the type of alternative you purchase, the chemical composition may vary and distinguish them further from natural stones. Diamonds that are physically grown in a lab will have an identical carbon composition to natural diamonds, giving them the same qualities (which also makes them subject to the possible impurities and imperfections as well). Alternative stones have different chemical compositions – ranging from zirconium dioxide of cubic zirconia stones to unique formulas of Nexus Diamonds™. While all stones that are grown in a lab are “real”, per say, their quality and appearance will be largely affected by the chemical composition.
Assessing Diamond Alternative Options
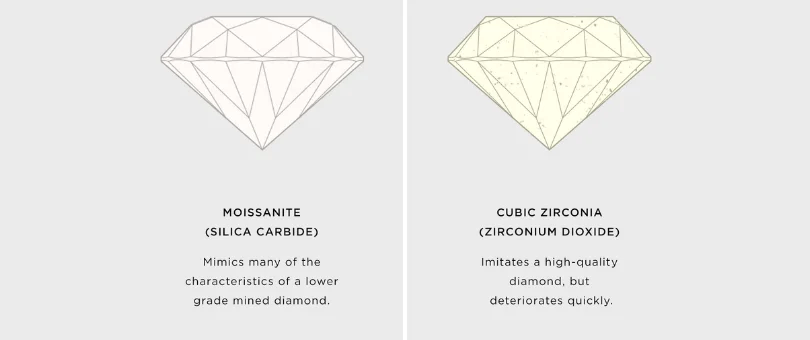
Two of the most common diamond alternatives are specifically important to understand in regards to quality factors – moissanite and cubic zirconia. While both offer an inexpensive option for consumers, they vary greatly in quality.
Moissanite
Moissanite is composed of silicon carbide, which mimics many of the characteristics of a lower grade mined diamond. The diamond shape or cut is designed to simply refract light, creating a visually appealing disco ball effect, and the diamond clarity and color of these stones cannot be consistently graded.
Cubic Zirconia
Comparatively, cubic zirconia is composed of zirconium dioxide which imitates a high-quality diamond, but deteriorates quickly. Within months, cubic zirconia’s color can become cloudy and yellow as it absorbs contaminants from its surroundings. As a result, neither option accurately represents the standards of a mined diamond or is considered an adequate alternative.
The 4 Cs of Nexus Diamond

When considering the question, “are lab diamonds real?” and attempting to find a diamond alternative that really does simulate the true beauty of a natural diamond, Nexus Diamond alternatives provide an answer to many of those musings. As noted, these diamond simulants are made with a patented formula base and coating that was specially created in order to produce stones of the highest quality across the 4C’s of the diamond scale.
Cut
What makes a diamond sparkle, the cut of a diamond is widely considered one of the most important characteristics to consider when making a purchase because a poorly executed cut can make even the rarest natural diamond appear dull and lifeless. In contrast, every Nexus Diamond alternative is created with an Ideal Cut to maximize the light reflected and achieve the best possible fire in the stone.
Color
The color of a mined diamond can vary from pure white and crystal clear to more of a yellow hue. This variation is graded on the diamond color scale, ranging from D, representing a complete lack of color, to Z which signifies that the stone has a noticeable yellow tint. Nexus Diamond alternatives are D grade and completely colorless, and this is consistent across all of the stones. In this way, the diamond alternative imitates the rarest of natural diamonds.
Clarity
The beauty of a diamond can be drastically altered by flaws found within and on the surface of a stone. These are known as inclusions and blemishes, respectively. Depending on the size and location of the flaws, a stone will receive a rating on the diamond clarity scale, ranging from Flawless, indicating that inclusions are tough to spot for even the most experienced gemologist, to Included, meaning that flaws are easily identifiable. Such defects occur naturally in mined diamonds, and are quite impossible to avoid in certain lab diamonds. Nexus Diamonds, on the other hand, all have a grade of Internally Flawless thanks to the controlled environment in which they are developed. This means that though the surface may have minuscule defects, the interior of the stone has no visible inclusions when viewed under 10x magnification by a skilled grader.
Carat
Where all diamonds, organic or lab-grown, are relatively the same is on the diamond carat chart. Regardless of their origin, all diamonds can come in various weights and sizes. Although, when diamond mining, a large stone will be much more difficult and rare to find. Contrastingly, lab diamonds can be manipulated to be different sizes in the gemological lab. In the case of a Nexus Diamond, nearly any carat weight can be produced.
Financial & Ethical Consideration

Traditionally, buying a diamond requires a significant investment depending on the stone’s quality of the stone as determined by the four characteristics listed above. The higher graded a single stone is on any of these qualities, the more valuable it becomes due to the rarity of finding such natural mined diamond. For example, a Flawless, grade D, 5-carat diamond is not likely to be found frequently when mining so when one of these qualities is uncovered, it is priced at tens of thousands of dollars. However, diamond alternatives are created with more control over these factors and resultingly, become less affected by rarity impacting price. Nexus Diamond alternatives can cost up to 90% less than an organic diamond of comparable quality.
There are other important costs associated with diamond mining, including the human and environmental impact. The methods traditionally used to mine diamonds are harmful to the environment, as strip mining practices and chemical runoff destroys habitats for decades to come. Plus, some traditional mines may force their laborers to work there while subjecting them to horrific working conditions. Thankfully, these environmental costs are almost entirely eliminated by the creation of lab-grown alternatives, as the sourcing practices are environmentally friendly and ethical.
Finding the right diamond can be one of the biggest journeys you embark on in fine jewelry purchasing, whether it’s to complete the perfect engagement ring or accent a beautiful piece of jewelry. With such an important decision, it’s imperative that you are equipped with the right knowledge to help you find the best choice. Mined diamonds can cost upwards of $10,000 to $15,000, due to their rarity and sourcing methods, though there is really no limit. Alternatively, a diamond alternative such as a Nexus Diamond will be much more affordable without sacrificing any of the quality. Are lab created diamonds real diamonds? Yes! You can rest assured that diamond alternatives like Nexus Diamonds provide all the beauty and brilliance of a natural stone without any of the added cost, monetary or otherwise.
*Diamond Nexus strives to provide valuable information, while being clear and honest about our products. The Nexus Diamond™ alternative is a patented lab grown stone that, among all simulants, most closely imitates the look, weight and wear of a mined diamond, with two exceptions – it is absolutely perfect in every way, and it costs significantly less. Price points and environmental facts expressed in this blog were taken from popular online retailers and may vary. Learn more about the environmental impact of mining by visiting out blog: blog.

