The Diamond Cut Scale: Your Guide to Choosing the Most Sparkly Diamond
November 8th, 2023 / Alese Oldenburg
Curious about the diamond cut? Learn everything you need to know before purchasing an engagement ring to make sure you pick the perfect stone. Diamond cut is one of the most important factors of a stone’s grade and will dramatically influence its price and quality. Preference for diamond cut grade will vary from person to person. While some may want a stone that’s as sparkly and fancy as possible, others may want a more modest and less glitzy style. It’s important to understand every aspect of a diamond’s cut before deciding if it’s right for you, as well as all of the factors that contribute to a stone’s overall quality. Learn these simple facts before beginning your search for engagement rings.
The 4Cs of Diamond Grading
Lab diamonds, mined diamonds, and the Nexus Diamond™ alternative are all graded on quality using the same scale: the 4Cs of Diamond Quality. This universal method was created by GIA (Gemological Institute of America) in the early 1940s, by founder Robert M. Shipley. He created this grading scale to provide training and knowledge to jewelers. Before this universal system was adopted, there was tremendous inconsistency between the technical terms merchants would use to describe colorless diamond characteristics. The 4Cs of diamond include: color, clarity, carat weight, and cut.

COLOR
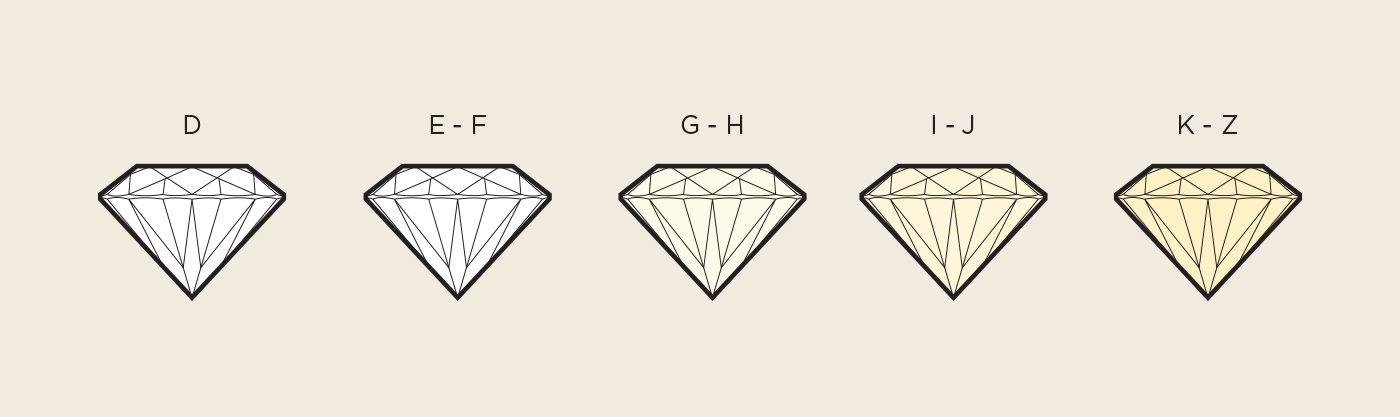
The D-to-Z diamond color scale is used to describe how many hues can be seen in a stone. It measures the lack of color, since diamonds are more valuable the clearer and less yellow they are. The color grade scale ranges from (D) colorless to (Z) light, which appears as a prominent yellow color. A chemically pure stone will have absolutely no hue, which is rare to find in the earth or create in a lab. Many of the color variations are so subtle that they appear invisible to the untrained eye. This is why many people opt for slight color, such as (G) or (H), because it is much less expensive and looks almost colorless.
CLARITY
This refers to the amount and placement of inclusions or blemishes that are seen in a stone.
There are six categories in the diamond clarity scale:
- Flawless
- Internally Flawless (IF)
- Very, Very Slightly Included (VVS1 and VVS2)
- Very Slightly Included (VS1 and VS2)
- Slightly Included (SI1 and SI2)
- Included (I1, I2 and I3)
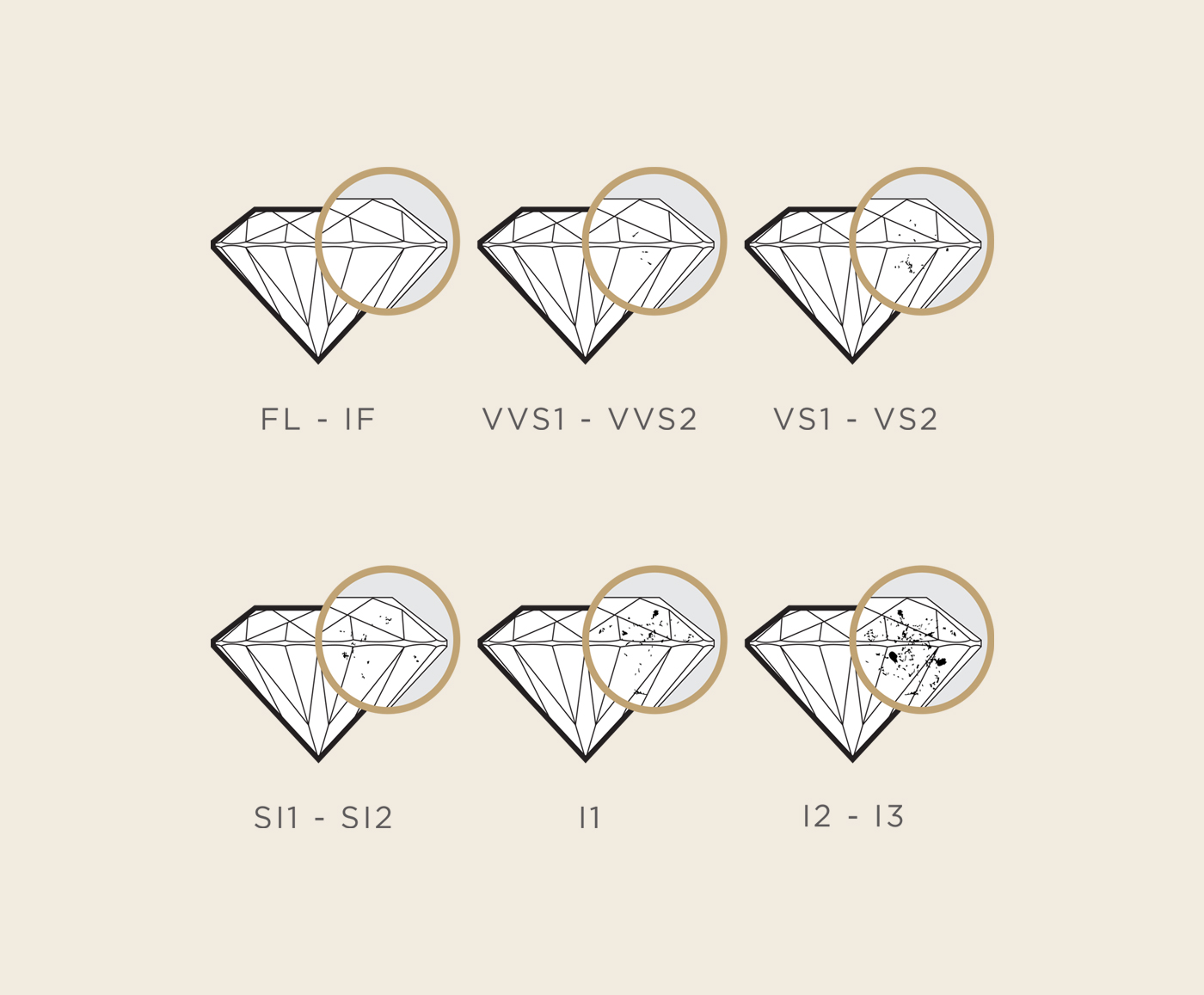
Many inclusions and blemishes cannot be seen by the average consumer. To the naked eye, a VS1 and a SI2 could look the same. Some inclusions can be hidden by prongs or other metalwork, resulting in a nearly perfect stone for much less money. Inclusions are caused when small crystals become trapped during a diamond’s formation. This is why they are seen in both mined and lab because they are produced under the same conditions of heat and pressure.
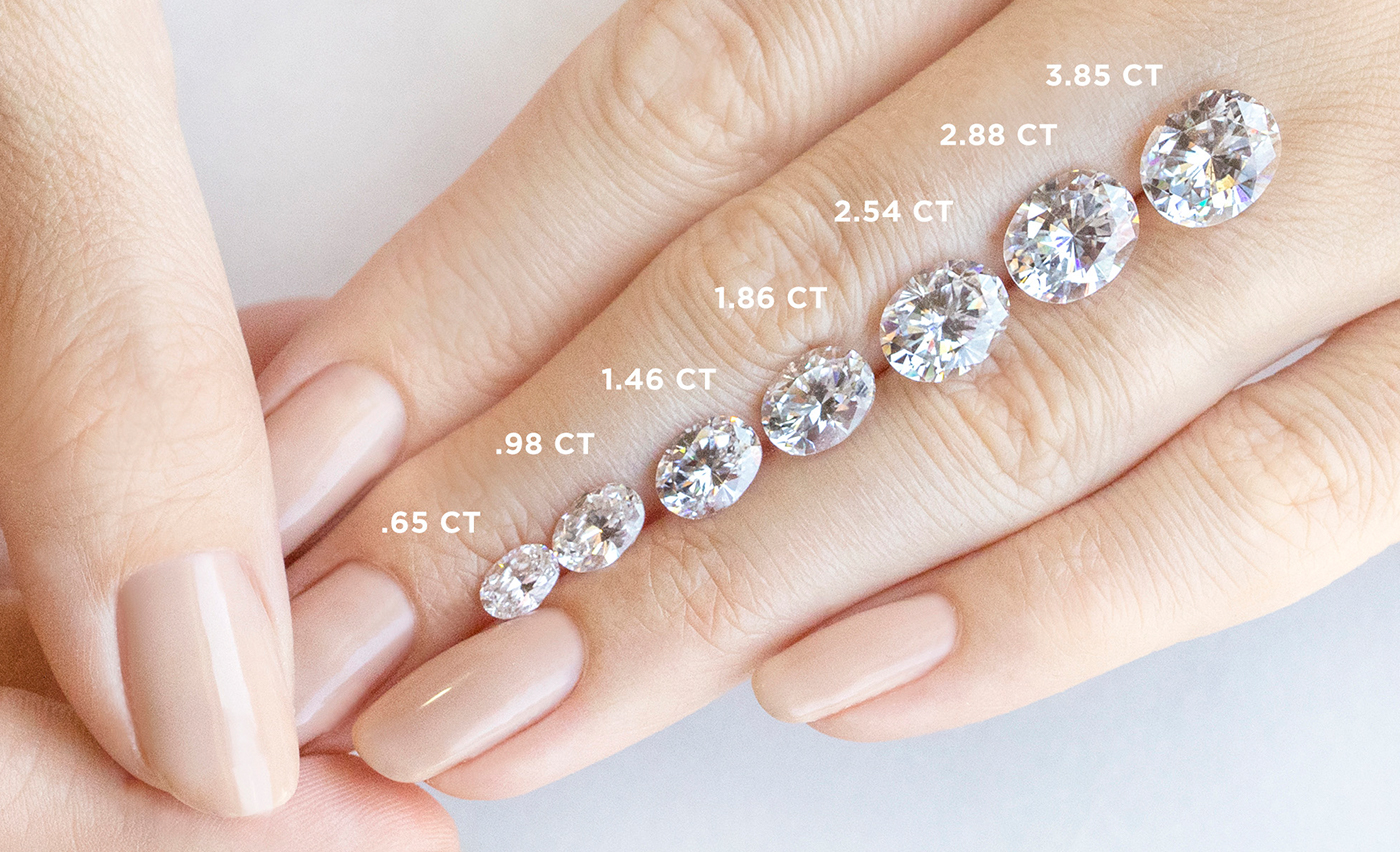
CARAT WEIGHT
Diamonds are measured by their apparent size. A metric “carat” is defined as 200 milligrams, and all stones are measured on the diamond carat chart. Price increases with carat weight because larger stones are more rare and more desirable. Size is not the only determiner of value, as each of the 4Cs plays an important part in determining price.

CUT
A diamond’s cut is arguably the most important of all the 4Cs and shouldn’t be confused with the shape of a stone. Cut refers to how well a diamond’s facets interact with light, resulting in their level of sparkle. A stone’s facets will be measured to examine brightness (internal and external white light reflection), fire (the scattering of white light into the colors of the rainbow), and scintillation (the amount of sparkle a diamond produces). So what is the best diamond cut?
The Cut Scale is measured by six categories
- Ideal: Ideal-cut diamonds represent the zenith of diamond craftsmanship. These gems are meticulously cut to exact proportions, resulting in the maximum brilliance and light dispersion possible. The precision required for this level of cut is unparalleled, making ideal cut diamonds a top-tier choice for those who demand the utmost in sparkle and radiance. However, their exceptional quality comes at a premium, with prices reflecting the painstaking craftsmanship invested in each stone.
- Excellent: Diamonds with an Excellent cut grade showcase exceptional craftsmanship. They are known for their remarkable brilliance and the remarkable way they disperse light. These diamonds capture the hearts of those seeking exceptional sparkle and beauty. While they may not reach the price levels of Ideal cut stones, they are still considered a high-end option, making them an attractive choice for those who appreciate the perfect balance between quality and value.
- Very Good: Diamonds in the Very Good Cut category boast excellent craftsmanship, offering a notable level of brilliance and light dispersion. They stand as one of the most sought-after choices among consumers. This popularity arises from their harmonious blend of quality and affordability. Very Good cut diamonds provide a dazzling appearance that satisfies discerning buyers without breaking the bank, making them a prevalent and sensible choice in the market.
- Good: A diamond with a Good cut demonstrates commendable craftsmanship, satisfyingly dispersing light and brilliance. This category represents a sought-after option for those with budget constraints. Good-cut diamonds strike an appealing balance between price and quality, delivering a pleasing level of sparkle without an excessive cost. This makes them an attractive choice for those who desire the charm of a well-cut diamond without a substantial financial commitment.
- Fair: Fair-cut diamonds exhibit average craftsmanship and disperse light and brilliance at a moderate rate. While they may not dazzle as brilliantly as higher-grade cuts, they offer a wallet-friendly alternative for budget-conscious buyers. Fair-cut diamonds are often chosen when the price is a primary consideration, as they provide the essence of a diamond without the premium cost associated with superior craftsmanship.
- Poor: Diamonds with a Poor cut have the lowest level of craftsmanship, resulting in minimal light and brilliance dispersion. These diamonds are the most economical choice, often favored by those with tight budgets. While they may lack the scintillation of higher-quality cuts, Poor-cut diamonds still possess the intrinsic beauty of a diamond. They cater to individuals who prioritize affordability and may be willing to trade some sparkle for financial prudence.
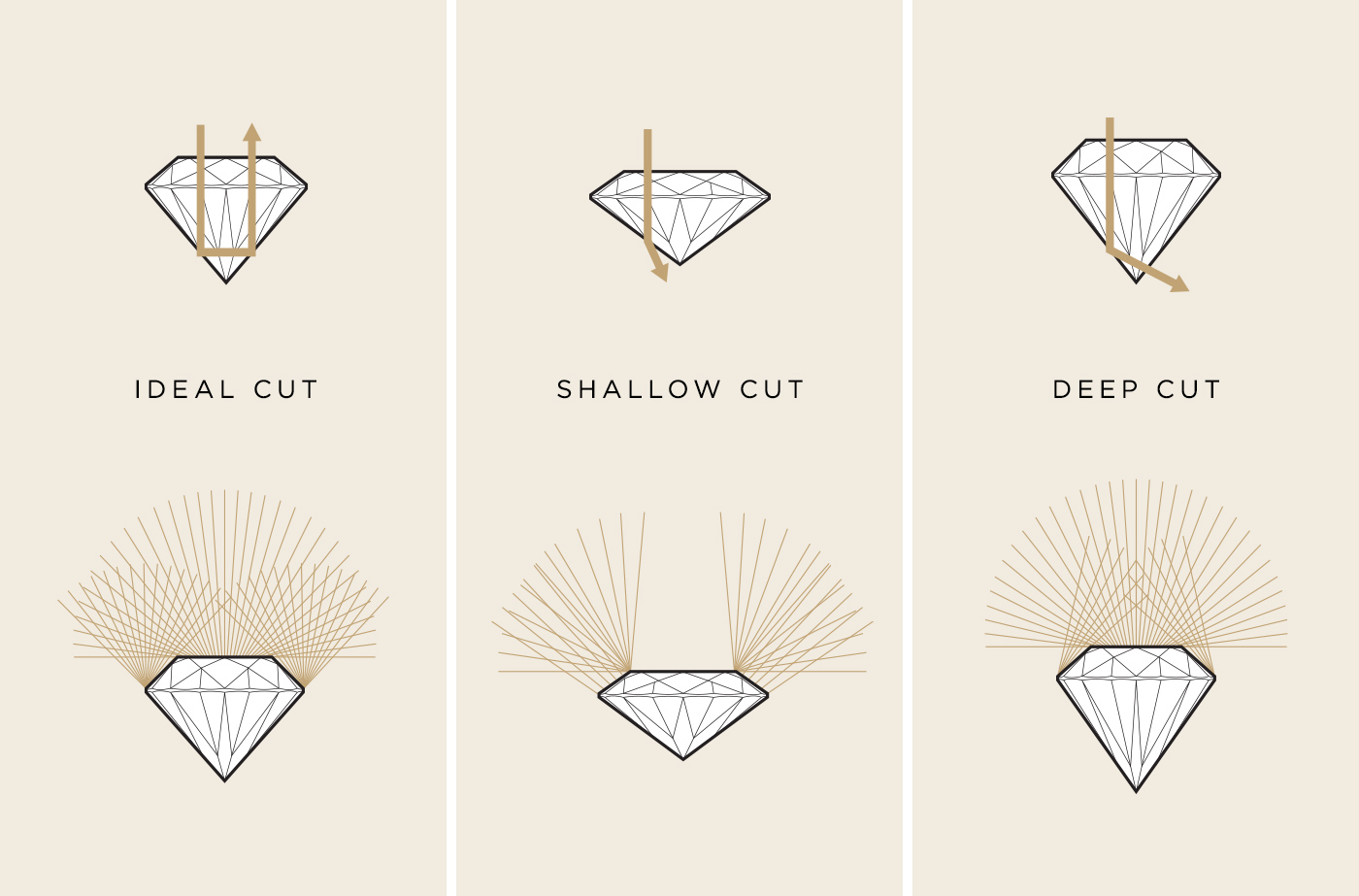
A Closer Look at Cut
Although a diamond’s cut does not refer to its shape, the shape of the stone does have an impact on how well light is reflected and refracted. This is due to how many, and the position, of a stone’s facets. It is well known that the classic shape, Round Brilliant, has the ideal facet pattern for the lightest return.
Round Brilliant cut is the most classic stone shape and is made up of 58 facets. Round engagement rings are by far the most popular of all the shapes as they’re the diamond cut that sparkles the most. Facets are the many flat surfaces you see that make up a stone’s geometric pattern. This shape follows the natural crystal shape of a rough diamond. The particular pattern of a Brilliant cut diamond was first developed by Marcel Tolkowsky, who came from a family of diamond cutters. This cut was precisely calculated to have maximum brilliance and dispersion of light.
 Although Round Brilliant returns the ideal amount of light, other shapes disperse light more uniquely. Step-cut shapes, like Emerald and Asscher, show long flashes of sparkle that resemble a staircase pattern. Other shapes, like Oval and Trillion, don’t have the extensive amount of brilliance that a round does but feature a much more modern silhouette.
Although Round Brilliant returns the ideal amount of light, other shapes disperse light more uniquely. Step-cut shapes, like Emerald and Asscher, show long flashes of sparkle that resemble a staircase pattern. Other shapes, like Oval and Trillion, don’t have the extensive amount of brilliance that a round does but feature a much more modern silhouette.
The Difference Between Cut and Shape
Cut is often confused with shape, although there is a big difference between them. Before you begin your diamond engagement ring search, learn the important facts to differentiate the two.
The type of cut a stone has refers to how well it returns light. The amount of light return has to do with the geometric facet pattern of a particular stone. The closer it is to an Ideal standard, the more sparkle it will emit. Stones are often more valuable and desirable the more light they return.
Diamond shape refers to the general silhouette of a stone when viewed face up. These are the common terms you hear such as Round Brilliant and Princess. Shapes are created to suit a variety of needs and continue to become more modern and unique. There are dozens of different styles, but only around 11 that are the most well-known.
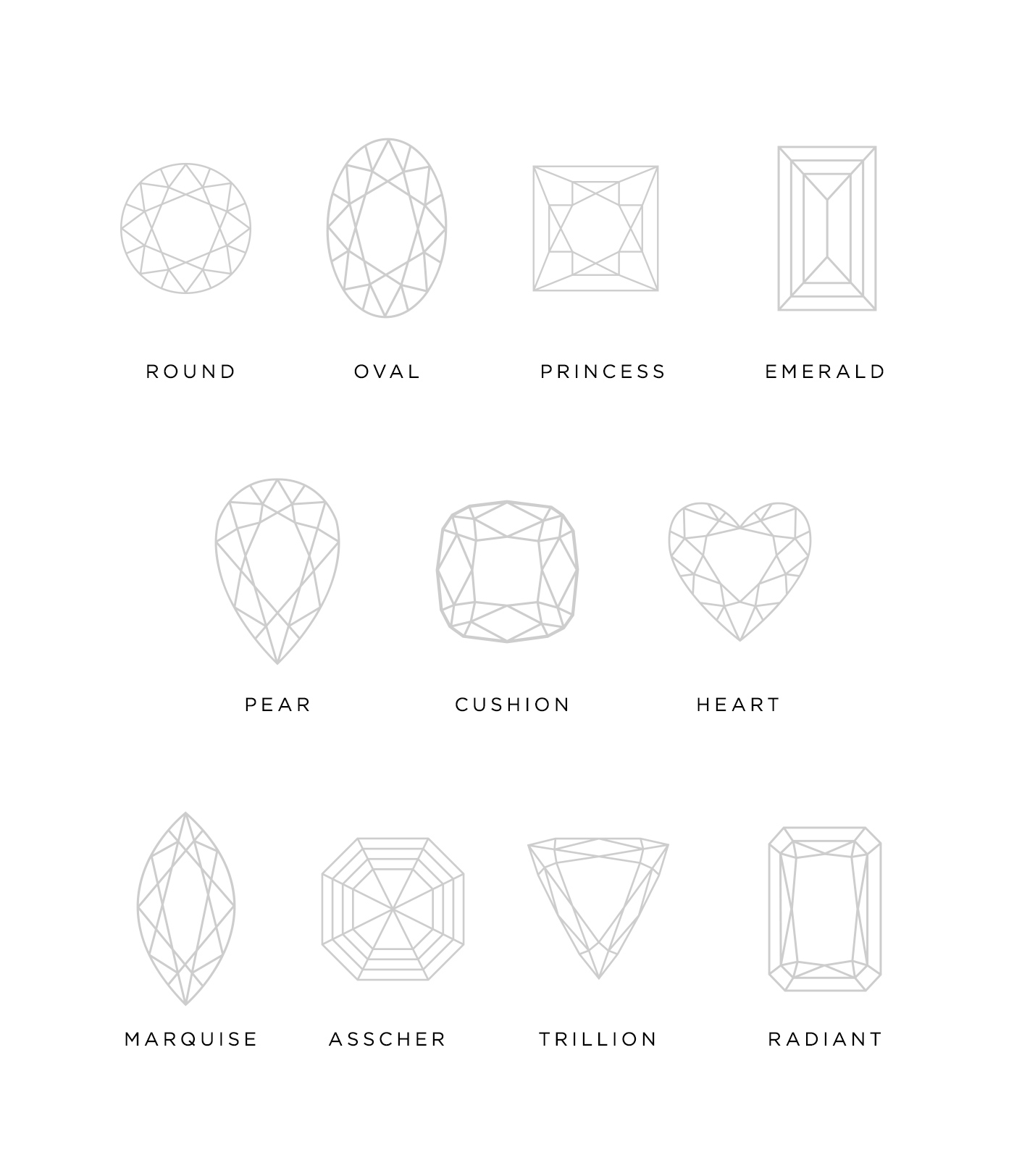
Types of Diamond Cuts and Shapes
- Round Brilliant: This is by far the most popular diamond shape because it returns the most amount of light due to its Ideal facet pattern. It resembles a simple circle, which makes it extremely versatile. The Round Brilliant cut diamond is renowned for its exceptional light return due to its precisely calculated facet pattern. Its near-perfect circular shape makes it incredibly versatile, complementing a wide range of jewelry styles. This timeless classic continues to be the most popular choice for engagement rings, offering unmatched brilliance and a symmetrical, elegant appearance that has captivated hearts for generations.
- Oval: Although similar to the shape of Round Brilliant, the Oval cut diamond is much more modern. It returns a great deal of light, almost to the extent of a Brilliant cut. The Oval cut diamond, while similar in brilliance to the Round Brilliant, introduces a contemporary twist with its elongated shape. Its unique proportions create an illusion of a larger size, making it a favorite among those seeking a balance between tradition and modernity. This shape’s ability to reflect light is nearly on par with the Round Brilliant, making it a captivating choice for those who appreciate a touch of sophistication.
- Princess: As the second most popular shape, the Princess cut diamond also similarly returns light to a Brilliant. Due to their square shape, their versatility is endless. As the second most sought-after shape, the Princess cut diamond is a square wonder that shares the Round Brilliant’s ability to sparkle brilliantly. Its clean lines and sharp corners add a bold, modern edge to any jewelry piece. Princess-cut diamonds offer endless versatility, making them ideal for both solitaire engagement rings and accent stones in intricate settings. The striking combination of symmetry and sparkle makes them a popular choice for contemporary brides.
- Emerald: The Emerald cut diamond is referred to as a step cut because it features long, open facets that resemble steps. This shape is similar to a rectangle and is featured in vintage designs. The Emerald cut, often referred to as a step cut, stands out with its unique, rectangular shape and long, open facets resembling steps. This vintage-inspired shape exudes timeless elegance and sophistication, making it a preferred choice for those who appreciate classic designs. The distinctive charm of the Emerald cut lies in its ability to showcase a diamond’s clarity and color, providing a window into its inner world of beauty.
- Pear: The pear shaped diamond is a modern style that is often seen in halo settings. It is known to have a slenderizing effect on fingers due to its tapered end. The pear-shaped diamond, resembling a teardrop, epitomizes modern elegance. Its distinctive silhouette gracefully tapers to a pointed end, creating a visually appealing shape that’s often seen in halo settings. Beyond its aesthetic appeal, the Pear shape is known for its flattering effect on fingers, giving them an elongated appearance. This blend of style and visual impact makes it a sought-after choice for those seeking a touch of sophistication.
- Cushion: The Cushion cut diamond shape is a modern interpretation of Princess. It features a similar square silhouette but has rounded corners which give it a pillow-like appearance. The Cushion cut diamond combines the best of two worlds, merging the square shape of the Princess cut with rounded corners to create a soft, pillow-like appearance. This modern interpretation of the classic Princess shape adds a touch of contemporary charm to traditional designs. The Cushion cut’s ability to balance clean lines with gentle curves makes it a versatile choice, suited for a variety of jewelry styles, from vintage-inspired to modern.
- Heart: The unique shape of the Heart is feminine and romantic. It is commonly seen in studs and engagement rings in a solitaire setting. The Heart-shaped diamond is the epitome of romance and femininity. Its distinctive silhouette, crafted with precision, captures the essence of love. This shape is commonly seen in stud earrings and engagement rings, often set in a solitaire style to emphasize its unique form. The Heart shape’s sentimental appeal and graceful lines make it a cherished choice for those seeking a symbol of enduring love and affection.
- Marquise: Similar to the pear-shaped diamond, the Marquise shape also has a slenderizing effect on the fingers, only more so due to tapered edges on both sides. Similar to the Pear shape, the Marquise cut diamond features an elongated profile, but with tapered edges on both sides. This elegant shape not only adds a touch of drama to jewelry but also creates a flattering illusion of longer fingers. Its elongated form allows for creative design options, making it a popular choice for unique and eye-catching pieces that beautifully balance tradition and modernity.
- Asscher: Also known as a step-cut, the Asscher cut features longer facets which give it a staircase appearance. It flashes long lines of sparkle, instead of the typical all-over sparkle. The Asscher cut, also known as a step-cut, captivates with its unique appearance featuring longer facets that create a mesmerizing staircase effect. Unlike traditional cuts with all-over sparkle, the Asscher cut diamond flashes long lines of brilliance, giving it a distinct and captivating allure. This shape is perfect for those who appreciate geometric precision and a vintage-inspired aesthetic, making it a remarkable choice for heirloom-quality jewelry.
- Trillion: Although it looks similar to the shape of a triangle, the Trillion shape features rounded edges that give it a smooth finish, popular in modern designs. The Trillion shape, often mistaken for a triangle, showcases rounded edges that provide a smooth and elegant finish. This shape’s versatility lies in its ability to fit seamlessly into modern jewelry designs. The Trillion cut is favored for its dynamic appearance, combining the geometric allure of a triangle with a touch of softness. Its unique aesthetic appeals to those seeking jewelry that stands out with contemporary flair.
- Radiant: The radiant cut diamond closely resembles the shape of an Emerald but has a brilliant facet pattern applied to the pavilion and crown which makes it shine with much more brilliance. The Radiant cut diamond offers the best of both worlds, merging the elegance of the Emerald shape with a brilliant facet pattern applied to the pavilion and crown. This fusion results in a dazzling display of brilliance that sets it apart. Radiant cut diamonds are prized for their luxury and captivating sparkle, making them a preferred choice for those who desire a touch of opulence and modern sophistication in their jewelry.
Finding the Perfect Stone
To find the perfect stone, take into account all 4Cs and shapes. When looking around, you’ll want to know each of the categories to make an educated buying decision. Buying online sometimes makes it easier to know this information, as it’s usually listed next to, or close to, the stone itself. Purchasing in-store from a jeweler may be harder as you’ll have to memorize the features of each stone you look at.
A tip to finding the perfect engagement ring is to first extensively research the company you’re thinking of buying it from. Aspects like what center stone you want and the price point you’re looking for, are good decisions to think about before you begin your search. If you have a stance on which stone you’re looking to buy, such as lab grown diamonds or mined, you’ll want to first find companies that offer those stones. Once you narrow that down, you can go on to your next decision, such as the maximum price you’re looking to spend. You can cross companies off your list that don’t fit your budget, and with each initial decision, you’ll begin to narrow your search before you even dive in. Ask yourself a few questions before heading into the purchasing decision.
WHICH TYPE OF STONE AM I LOOKING FOR?
There are multiple stone options in the market today, which consist of mined diamonds, lab grown diamonds, and diamond alternatives. Stone types may come from different origins and differ in composition, which is why it can be helpful to do some research. By finding the answer to the question, how are diamonds made, you will learn how distinctions in composition can have a large impact on quality, appearance, and price. This can help you decide which option is right for you.
WHAT AM I LOOKING TO SPEND ON AN ENGAGEMENT RING?
Start by creating a range. The average one-carat mined solitaire engagement ring is around $6,500*, but the same ring set with a lab-grown diamond could cost between 20-30% less. It may be helpful to push the high end of your budget, as you don’t want to rule out the perfect diamond ring just because of a minor price difference. Plus, most companies today offer different payment and financing options to help accommodate your budget.
WHAT GUARANTEES AM I LOOKING FOR IN A PURCHASE?
This is an especially important one because every company differs. If you know you would like a grace period after buying to ensure you made the right decision, research the return period of the company or jeweler you’re thinking of purchasing from. 30 days is the average period for online retailers, which will allow you the option to see it in person before deciding if it’s the right one or not.
WHAT ARE THE MOTIVATIONS BEHIND THE COMPANY I’M LOOKING TO PURCHASE FROM?
Although this may be insignificant to some, the diamond business can be a brutal one, which is why this is such an important question. If you choose to buy mine, research the ethical and environmental factors your buying decision will contribute to. The same goes for lab grown diamonds. Not all companies have the same ethical standards, and you should be confident in your decision since your diamond jewelry purchase will be cherished for a lifetime.
*Diamond Nexus strives to provide valuable information, while being clear and honest about our products. The Nexus Diamond™ alternative is a patented lab created diamond simulant that, among all simulants, most closely imitates the look, weight and wear of a mined diamond, with two exceptions – it is absolutely perfect in every way, and it costs significantly less. Price points and environmental facts expressed in this blog were taken from popular online retailers and may vary. Learn more about the environmental impact of mining by visiting out blog: blog.

