Lab Diamonds vs Real Diamonds – Unveiling the Differences
December 4th, 2023 / Alese Oldenburg
Lab grown diamonds, the modern alternative to natural diamonds, possess the same timeless style and sparkle that have been revered for centuries. A mark of significant moments, lab diamond engagement rings make for the perfect symbol of love and commitment. These ethically sourced stones hold the same physical properties as their natural counterparts, creating a focal piece that inspires an entire look or adds subtle sparkle to any outfit. Whether an heirloom piece for special events or a new ring to pop the question, lab grown diamond jewelry is the perfect answer for every occasion.
However, even with the beauty and joy that it promises, diamonds can also be a significant financial investment. When you’re looking for your ideal diamond – whether choosing an engagement ring or another piece of jewelry – there can be a lot of pressure to find the best option at a price point you can afford.

The positive news is that today there are more options than ever in the diamond industry, which makes the search for the perfect diamond much more approachable. There is a wide variety of synthetic and man-made diamonds, which are created in a lab and often offer a very similar look and feel to naturally mined diamonds, but at an affordable price.The rise of these diamond alternatives in engagement ring trends and other jewelry has also brought along an increase in conversation about whether a diamond is real or not and how various alternative options differ. Many often wonder, what is a lab created diamond? And, are lab grown diamonds real? To better inform your shopping decisions, it is important to understand the difference between lab created diamonds and real diamonds, from the perspective of quality, ethics, and affordability.

Lab Grown Diamonds vs Real
The diamond industry has been dominated by naturally mined diamonds due to their brilliance and durability. While simulated lab created diamonds have only appeared on the market relatively recently, they provide a competitive alternative for diamond alternative rings and jewelry, not just for quality, but especially in regards to price and environmental impact. It’s for this reason that many people turn to simulated lab diamond engagement rings and lab grown diamond wedding bands The key differentiating factors between manufactured diamonds and real diamonds lie in the sourcing, quality factors, and cost.

Source & Composition
Over the past decade, there has been an increasing awareness of environmental changes and human working conditions around the world. With this, consumers have also started to realize the power of their buying decisions, and how that can have an impact on those issues. Consumer purchasing changes have been seen in the diamond market in particular, as people have discovered the source of diamond alternative options.
As many are aware, natural diamonds are created in the land beneath the Earth’s surface. At depths close to 100 kilometers underground, they are made of pure carbon and formed from being under intense pressure at a very high temperature for billions of years.
However, what some people may not know is the danger associated with mining diamonds from the land. The consistent and strong demand for diamonds has led to practices that are destructive to landscapes, habitats, and wildlife. Many diamond mines have had to turn to new land in order to source additional diamonds to meet demand, and if an ecosystem is on that land already, it’s disregarded for the sake of mining. In addition to habitat destruction, this practice results in immense land displacement, extremely high energy expenditure and other longer-term consequences like acid rock drainage. Moreover, many diamond mining practices utilize dangerous employment practices – ranging from unsafe labor practices to outright human rights abuses.

While the source of all lab diamonds is ecological and conflict-free, there is a range of lab diamond options that vary greatly in composition. Lab diamonds have the same chemical composition as natural diamonds. This results in diamonds with the same optical and chemical properties as those formed in nature as well.
On the other side of the lab diamond scale, Moissanite diamond simulant and cubic zirconia are composed of alternate chemical substitutes, which results in a stone that is different from natural diamonds in both appearance and quality. Moissanite engagement rings are known for their unique optical qualities which are sometimes referred to as the “disco ball effect.
Irrespective of the variation in diamond quality, lab grown diamonds overall are able to keep up with high market demand at a far smaller impact on the earth and human nature.
When considering the real diamond vs lab diamond options, there are two things you should know. First of all, lab diamonds are chemically identical to real diamonds—yes, this means they’ll also test as a diamond. Secondly, think about the power that your buying decision has to impact the progress on the environment and ethical sourcing.
Size
The size of this precious stone is considered one of the most important features because it has an enormous impact on the brilliance and the sparkle of a diamond. The size is measured by a diamond’s weight, which is known as the carat size. Carat weight is a very important measurement in natural diamond grading because it varies so widely and has a high impact on cost. The cost of natural diamonds rises exponentially depending on their carat weight, which is a result of the mining method because it is rarer to find larger diamonds. For example, a one-carat diamond can cost up to five times more than a half-carat diamond of the same purity and color.

Contrastingly, the sustainable production of lab grown diamonds makes it so that diamonds at a range of carat sizes can be created at a lower price. The selling price will vary across lab grown diamond options since the other quality factors of the diamond will have an effect on value too. Overall though, consumers won’t have to compromise as greatly on diamond size with lab diamonds when weighing affordability with size.
Clarity
Wondering how to tell if a diamond is real or lab grown? One of the main optical differences between a man made diamond and a real diamond is the clarity of each. Diamond clarity is the assessment of the surface flaws, or blemishes, that are found internally and on the surface of a gem. It is measured on an 11 point clarity scale established by the Gemological Institute of America (GIA). The scale ranges from FL – flawless & perfect clarity – to I3 – imperfect with many inclusions and low quality.
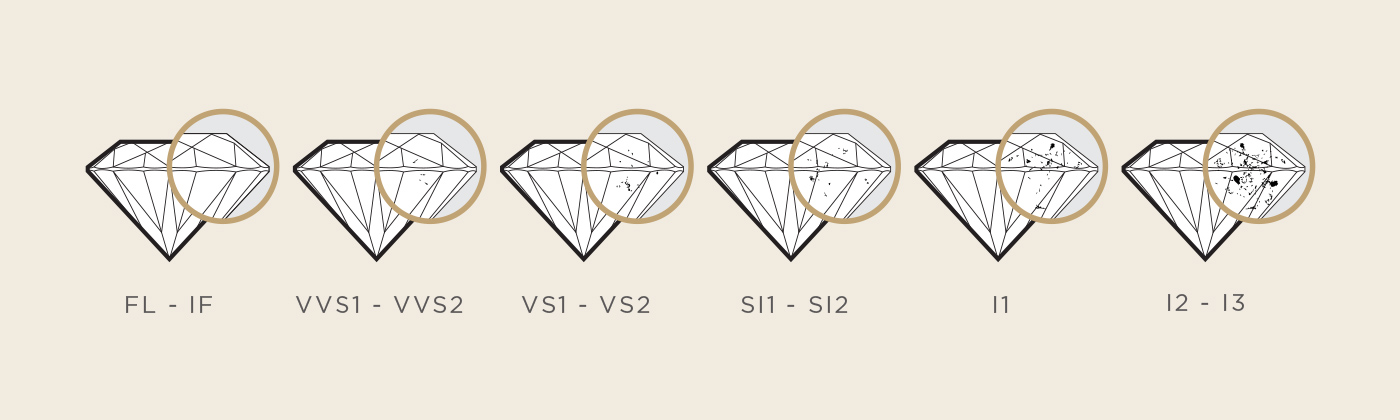
The gemological creation of natural diamonds results in stones that vary greatly in size, color, and levels of clarity. The majority of natural diamonds will have some imperfections. Flawless diamonds are rare to find, and therefore are extremely expensive. Wherever an earth mined diamond falls on the clarity scale will have a direct impact on its value.
On the other hand, the ability to specifically alter certain qualities of a diamond in a lab creates the opportunity to make diamond alternatives that are entirely free of imperfections and blemishes, unlike an earth mined diamond. Similar to other qualities of manufactured diamonds, the clarity will vary across the different lab diamond options. When comparing the difference between cubic zirconia and simulated diamonds, a key factor is that cubic zirconia will appear flawless at first but will take in contaminants from the environment over time. The Nexus Diamond simulants are created to be IF rated (internally flawless) and will remain that clarity forever. It can be helpful to research the clarity characteristics of different lab diamonds alternatives when comparing options.
Color
The color of a diamond is a measure of its degree of transparency, which in turn influences how bright and beautiful the diamond appears. It is measured with a scale that ranges from the letter D (colorless) to Z (yellow or brown).
The first three categories, “D,” “E” and “F” are colorless, and therefore also the most expensive because that is the most highly desired color value. The categories “G,” “H,” and “I” are almost colorless, and “J,” “K,” “L,” and “M” show a very light color.
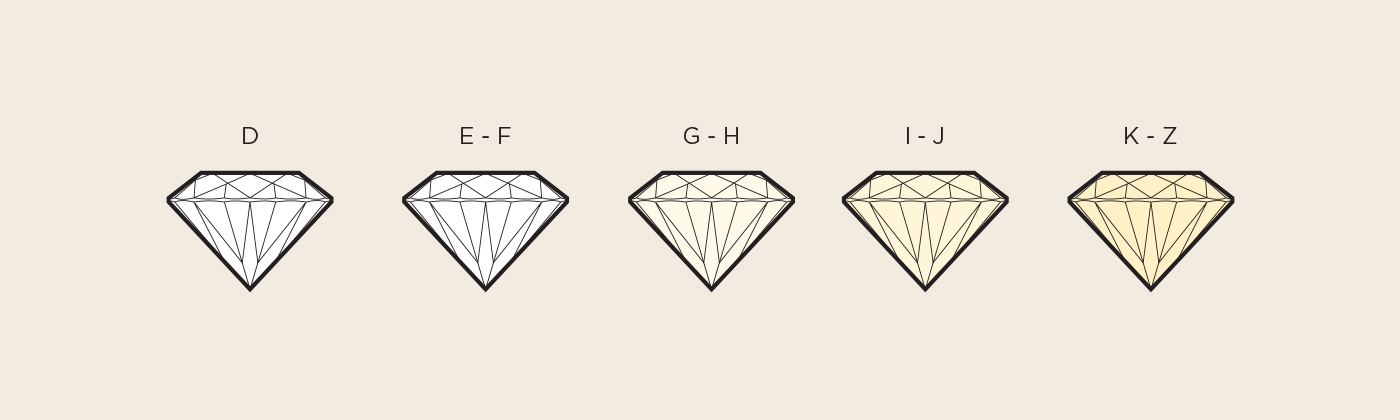
To see the color of a diamond, you must observe it diagonally against a white background. Only an expert under special lighting conditions can distinguish the degrees of color (for example, between F and G), but with a little practice, most people can detect the difference between colors that have several degrees of variation (for example, between F and I).
Usually, a natural diamond will be somewhat yellow, due to the hydrogen atoms in its structure. It is very rare to find a total absence of color in a diamond, so completely colorless stones have much more value.
Similar to clarity, lab diamonds can also be created to have a certain color. Due to the unique chemical composition, different lab diamonds will have distinct colors as well. The patented chemical structure of Nexus Diamond simulants creates a stone that will always be “D” rated and completely colorless. Other options such as Moissanite and cubic zirconia are either not consistently graded for color or will decrease in color quality over time.
Cut
The diamond cut scale applies to how each stone is cut and the resulting angles and proportions. It’s important not to confuse cut with shape – such as “round”, “princess” or “square” – because they are distinct.
A good cut is essential for a diamond’s brightness because it will impact how the light is reflected from the stone. If a diamond is poorly cut, the light will escape from the sides of the stone, causing it to lose much of its brightness.
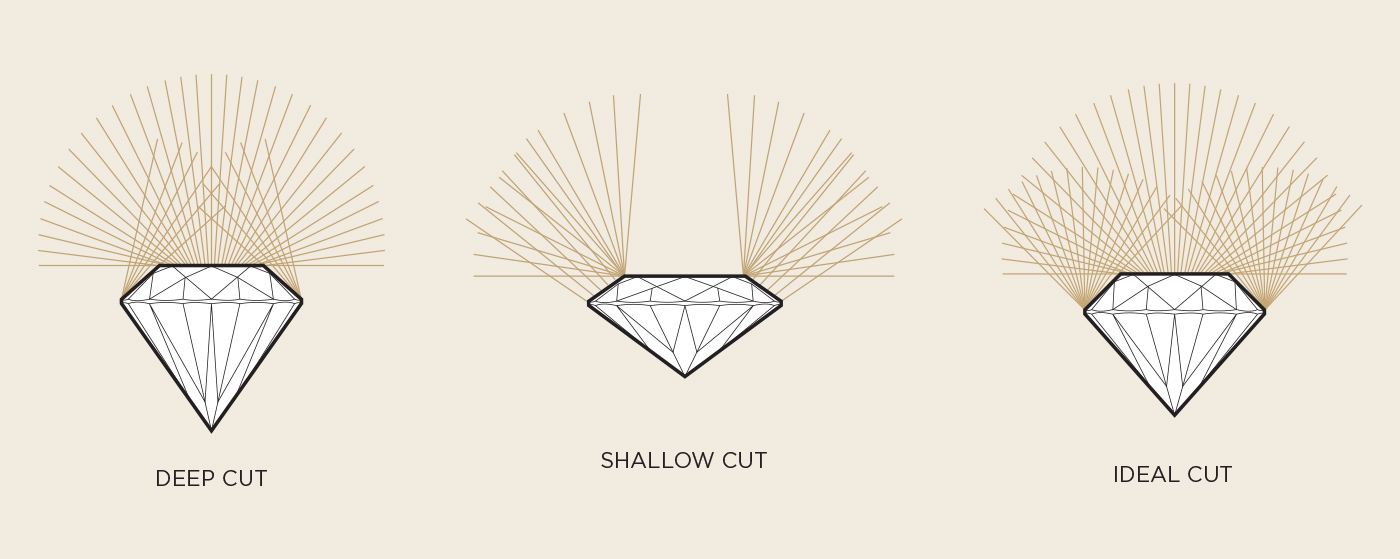
In addition to the perfection of the cut, the beauty of the stone is influenced by its symmetry and the quality of its polish. Both are factors that, like the quality of the cut, significantly affect the brightness of a diamond and its ability to reflect the light that falls on it.The quality of the cut is measured on the following scale, established by the GIA:
- Excellent
- Very Good
- Good
- Fair
- Poor
The cut is an important characteristic to compare when assessing lab diamonds and natural diamonds. A natural diamond depends on the cut for its sparkle, and there is a vast range of cut quality due to the mining practice. Similar to the scales of clarity and color, diamonds at the higher end of the scale for the cut are rare and will significantly increase in price.
In contrast, lab diamonds can be more closely manipulated for a perfect cut. Some will still vary in cut based on the technological processes used to produce the diamond and due to the difficulty in truly achieving an excellent cut. Diamond Nexus creates diamond simulants that are always the highest cut level in order to achieve maximum sparkle and luminosity.
The Final Differentiator – Cost & Ethics
The differences between lab grown diamonds vs natural diamonds may be confusing upon first consideration, but once the major differentiating factors are understood, the choices become quite clear.
The most straightforward factor when considering diamonds is how all of the quality characteristics have a direct relationship to the cost and the original sourcing method.
Many people wonder the right answer to how much to spend on an engagement ring, making price one of the most significant determinants in buying diamond jewelry. Prices will vary widely depending on size, clarity, color, and cut. This can make buying a diamond a prohibitive purchase if you have to compromise on quality in order to find something in your price range.
This is where lab diamonds have a great advantage because the production method creates diamond options for which quality will not have to be weighed as strongly against price.
Not only do the sourcing methods for a lab grown vs real diamond have a direct correlation to cost, but they also are tied to environmental and ethical consequences as well. Natural diamonds have an immense ecological impact and contribute to perpetuating the use of horrific labor conditions for workers. In stark contrast, the practice of creating lab diamonds is both eco-friendly and conflict-free.
Natural, mined diamonds have been the standard of the industry for centuries. However, we are entering an era where that market is transforming. For the first time, consumers have the opportunity to find brilliant, flawless diamonds that are affordable and have the power to impact practices around the world.

*Diamond Nexus strives to provide valuable information, while being clear and honest about products. The Nexus Diamond™ alternative is a patented lab grown stone that, among all simulants, most closely imitates the look, weight and wear of a mined diamond, with two exceptions – it is absolutely perfect in every way, and it costs significantly less. Price points expressed in this blog were taken from popular online retailers and may vary. Learn more about the environmental impact of mining on our blog.

